A bowl of kimchi, a fermented vegetable facet dish that may be a staple in all Korean meals
Kitzcorner | Getty Photographs
You might have heard of the “Korea low cost” in South Korea’s inventory markets. Now, prepare for the “kimchi premium,” named after the favored facet dish of fermented greens that is a staple in Korean delicacies.
The “kimchi premium” refers back to the value hole in cryptocurrencies, particularly bitcoin, when listed in South Korea versus these listed in U.S. or European exchanges.
Whereas this might be seen as an arbitrage alternative for some, it is not really easy to make a fast buck.
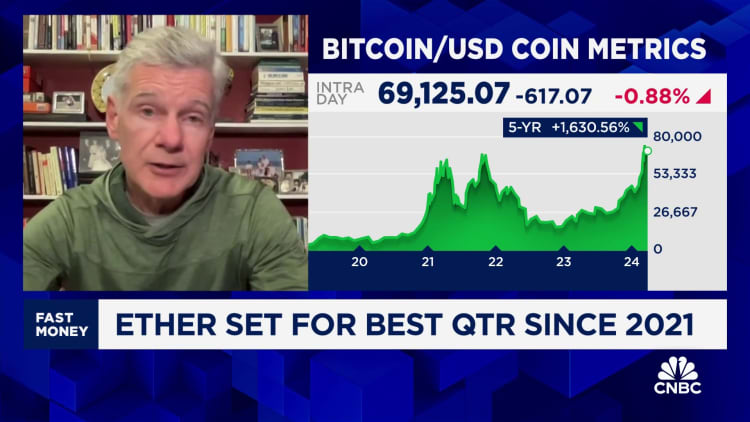
The kimchi premium is within the highlight once more after bitcoin reached all-time highs in mid-March, hovering previous $73,000 to a report excessive on March 13, in line with Coin Metrics information. The digital foreign money has since fallen beneath the $70,000 degree.
As bitcoin examined new highs, the kimchi premium additionally soared. In keeping with cryptocurrency information supplier Cryptoquant, the Korea Premium Index reached its highest degree since Might 2021 on March 16, reaching 10.88%.
Meaning bitcoin’s buying and selling value in South Korea was roughly 10% larger than the worldwide spot value.
Again in 2017, FTX founder Sam Bankman-Fried noticed an arbitrage alternative within the value hole throughout totally different exchanges. The CEO of failed crypto trade FTX was final week convicted for crypto fraud and sentenced to 25 years in jail.

As a quant dealer in 2017, he observed the worth discrepancy of bitcoin might generally be as a lot as 60%. The arbitrage alternative was particularly compelling in South Korea, the place costs there have been considerably larger than in different international locations.
He went on to launch his proprietary buying and selling agency Alameda Analysis to start out buying and selling the digital foreign money full time, raking in 1,000,000 {dollars} a day in some instances.
In 2022, the then 30-year-old billionaire informed CNBC he was drawn to the business as a result of the broad arbitrage alternatives appeared “too good to be true.”
The ‘premium’
Bitcoin steadily trades at the next value in South Korea in comparison with different markets, in line with analysis by the College of Calgary.
Whereas the typical kimchi premium was 4.73% between January 2016 and February 2018, it hit ranges as excessive as 54.48% in January 2018, in line with the report that was printed in 2019.
Why is there a value discrepancy?
It happens as a result of crypto, in contrast to shares or bonds, are decentralized digital property which use blockchain expertise that is not managed by a government, and may due to this fact be traded at totally different costs world wide.
One issue for the worth hole is the excessive demand for cryptocurrencies in South Korea, in what has generally been known as “a closed market surroundings.”
To stop cash laundering in crypto buying and selling, the nation’s Monetary Companies Fee has carried out what is called a “actual identify” coverage, requiring an individual’s home digital asset buying and selling account identify to match the identify on their deposit account with a financial institution.
Solely South Korean nationals or foreigners with resident registration playing cards are allowed to open full-fledged financial institution accounts within the nation, successfully locking out abroad entry to its home crypto exchanges.
“South Korea requires a particular kind of checking account linked to a person with a purpose to open a crypto trade account, which makes it difficult for institutional gamers to enter the crypto market,” Crypto information platform Chainalysis mentioned in a 2023 report.
Bitcoin costs in South Korea are pushed above these in different international bourses, as demand is pushed primarily by retail traders since institutional and international traders are usually not capable of take part freely.
Chainalysis added South Korea acquired a complete crypto worth of over $111.82 billion from July 2022 to June 2023 — the most important quantity in any East Asian international locations, surpassing even Japan and China, the area’s largest economies.
The report additionally famous that South Korea seems to be the least institutionally pushed market in East Asia based mostly on transaction sizes.
“That is doubtless because of native rules that make it troublesome for monetary establishments to commerce,” the report mentioned.
Arduous arbitrage
The kimchi premium might seem like an arbitrage alternative, nevertheless it’s not so simple.
In idea, an investor should purchase bitcoin on a world trade at a lower cost, switch the cryptocurrency to a South Korean bitcoin trade at the next value, and make a risk-free revenue by promoting it on the South Korean trade.
Nonetheless, the truth that the South Korean gained is regulated makes this arbitrage technique troublesome for worldwide traders, defined Baik Seunghoon, nation supervisor for South Korea with crypto mining agency GoMining.
He identified that the gained is a extremely restricted foreign money, and gained transfers exterior the nation are tightly managed.
Citing South Korean capital controls, Baik identified that so-called “small abroad remittance companies” are solely allowed to remit as much as $10,000 per transaction for every particular person, as much as an collected quantity of $100,000 for a similar individual per 12 months.
This implies there’s a restrict to how a lot fiat foreign money could be taken out, which by extension, limits the speed of good points that merchants can money out.
There are additionally different dangers to this arbitrage technique, in line with analysis by College of Calgary.
First, the switch of bitcoin from a international trade to a South Korean trade takes time, and throughout that point, the value of bitcoin might change.
Checks by CNBC revealed that transfers can take wherever from one hour to in the future for cryptocurrencies to be shifted to an exterior pockets.
Which means that traders run the chance of seeing the kimchi premium develop into smaller or utterly disappear through the time it takes to execute the arbitrage commerce.
Paul Brody, international blockchain chief at EY, informed CNBC that whereas the kimchi premium has been round for some time, his view is that it is more durable to conduct the arbitrage commerce in the present day than prior to now.
“What’s totally different now’s that in lots of different components of the world, it’s an increasing number of troublesome to ship cash by way of the blockchain with out doing any KYC,” Brody identified. He was referring to the know-your-client course of, the place clients’ identities should be verified by monetary establishments in order to mitigate monetary crime.
Moreover, he mentioned exchanges which are compliant with rules will restrict an investor’s capacity to ship cash abroad until an investor has the mandatory documentation and regulatory help.
Briefly, the truth is that point, charges and capital controls can introduce problems, making capitalizing on this technique both much less enticing or outright unviable.
— CNBC’s MacKenzie Sigalos and Kate Rooney contributed to this report.







